Prostate Cancer: Risk Factors and Prevention You Should Know Now!

Prostate cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers in men worldwide, affecting millions of individuals every year. It is a serious health concern that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life and longevity, and early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.
- Prostate Cancer: Symptoms and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options
- Navigating Life With Prostate Cancer
- Takeaway
This article will explore the basics of prostate cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also discuss ways to reduce your risk of developing this condition and highlight the importance of regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Prostate Cancer: Symptoms and Risk Factors

Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped gland in the male reproductive system. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men, with approximately 1 in 8 men being diagnosed with this disease during their lifetime.
Statistics
According to the American Cancer Society, an estimated 288,300 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in the US, and around 34,700 deaths from the disease in 2023.
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men, after lung cancer. The average age at diagnosis is 66 years old, and more likely to develop in older men.
Approximately 1 in 41 men will die from this disease. Although it is a potentially fatal disease, most men diagnosed with this disease survive thanks to early detection and treatment advancements.
Symptoms
In its early stages, this type of cancer often does not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as cancer grows and spreads, it can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak urine flow
- Pain or burning during urination
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
- Erectile dysfunction
Risk Factors
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing this type of cancer, including:
- Age: The risk of developing this disease increases as men get older.
- Family history: Men with a family history of this disease are at a higher risk of developing it.
- Race: African American men are more likely to develop this type of cancer than men of other races.
- Obesity: Obese men are at a higher risk of developing aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Men who are exposed to certain chemicals, such as Agent Orange, may be at an increased risk of developing this type of cancer.
Treatment Options
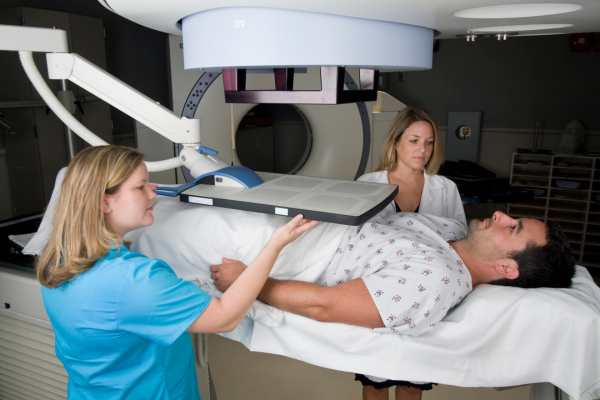
The treatment options for this disease depend on various factors, including the stage of cancer, the patient's age and overall health, and the patient's personal preferences. Here are some of the common treatment options:
Active surveillance
For some men with early-stage prostate cancer, active surveillance may be an option. This involves close monitoring of cancer, with regular check-ups and testing, to see if it is growing or becoming more aggressive. If cancer begins to progress, other treatment options may be considered.
[content-egg module=AmazonNoApi template=list]
Surgery
Surgery to remove the prostate gland, known as a prostatectomy, is a common treatment option for prostate cancer. This can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. This can be done externally, with a machine that directs radiation beams at the prostate, or internally, by placing small radioactive pellets inside the prostate.
Hormone therapy
Prostate cancer cells rely on hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. Hormone therapy involves blocking the production or action of these hormones to slow or stop the growth of cancer cells. This can be done through medications or surgery to remove the testicles (where testosterone is produced).
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. It is typically used in advanced cases of prostate cancer when cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This is also a common treatment for all types of cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a newer treatment option for prostate cancer that works by boosting the immune system to fight cancer cells. It is typically used in advanced cases of prostate cancer.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, such as the stage of cancer, the patient's overall health, and their personal preferences. A healthcare professional can help guide the patient in choosing the best treatment option for their specific case.
Navigating Life With Prostate Cancer
Being diagnosed with prostate cancer can be overwhelming and may significantly impact a person's daily life. However, there are several ways to manage life with prostate cancer, including the following:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle
Eating a healthy diet, staying physically active, and managing stress can help improve overall health and well-being. Additionally, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Regular check-up
It is essential to maintain regular check-ups and communicate openly with your healthcare team about any symptoms or concerns. This can help ensure that your treatment is effective and that any complications are identified and treated promptly.
Practicing self-care activities such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Seek support
It can be helpful to talk to a support group, a mental health professional, or a loved one about the emotional impact of prostate cancer. Seeking support can help alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression.
Prostate cancer treatment can cause side effects such as fatigue, urinary incontinence, and erectile dysfunction. Work with your healthcare team to manage these side effects and improve your quality of life.
Takeaway
Managing life with prostate cancer can be challenging, but it is possible to maintain a good quality of life with the help of proper treatment, lifestyle modifications, and support from healthcare providers and loved ones.
Prostate cancer is a common disease that affects many men. Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes and maintaining a good quality of life. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for prostate cancer, men can take an active role in their health and well-being.
Remember to take care of your health by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, seeking regular check-ups, and communicating openly with your healthcare team. With the right support and care, it is possible to manage prostate cancer and live a fulfilling life.
ActiveMan — Make Your Move
The Modern Guide to Men’s Health, Fitness & Lifestyle.





