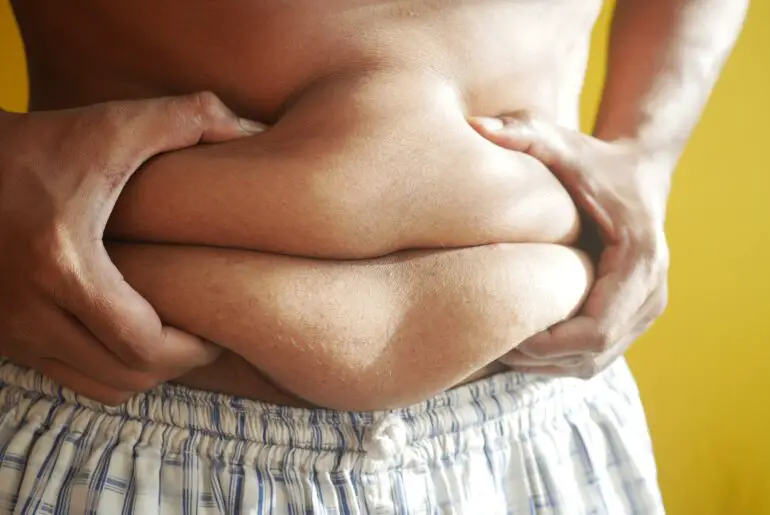
Visceral fat, often dubbed as “active fat,” resides deep within the abdominal cavity. This type of fat wraps around vital organs like the liver, pancreas, and intestines. Unlike subcutaneous fat found just beneath the skin, visceral fat poses significant health risks.
Research indicates that excessive visceral fat increases the likelihood of developing serious conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Understanding how to reduce visceral fat is crucial for improving overall health and well-being.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Visceral Fat: Visceral fat is harmful as it surrounds vital organs, increasing health risks.
- Spotting Visceral Fat: Look out for a protruding belly or a thicker waistline as signs of excess visceral fat.
- Healthy Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise and stress management can help reduce visceral fat levels effectively.
- Smart Dietary Choices: Opt for a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats to combat visceral fat accumulation.
- Behavioral Modifications: Adequate sleep and mindfulness practices can aid in reducing stress and preventing visceral fat build-up.
- Practical Implementation Tips: Start small by incorporating daily walks, meal prepping, and seeking professional guidance for personalized strategies.
Defining Visceral Fat
Health Risks
Visceral fat poses risks for diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. It impacts overall health by increasing inflammation and insulin resistance. The correlation between visceral fat and chronic conditions is strong, leading to long-term health issues.
Causes
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise contribute to visceral fat accumulation. Genetic predispositions can also play a role in excess visceral fat storage. Hormonal imbalances, especially an increase in cortisol levels, can lead to the gain of visceral fat.
Normal Levels
Healthy ranges of visceral fat are around 1-12% for men and 10-25% for women. Age and gender influence these levels, with older individuals typically having higher amounts. Maintaining optimal visceral fat levels is crucial for health as excess visceral fat increases the risk of various diseases.
Identifying Presence
Physical Signs
Excessive visceral fat often manifests through physical signs such as a protruding belly or love handles. These visible indicators can signify high levels of visceral fat accumulation in the body. Abdominal measurements, especially waist circumference, serve as a practical tool to gauge the presence of visceral fat. A larger waist size is commonly associated with increased visceral fat content, indicating potential health risks.
Body composition analysis plays a crucial role in identifying visceral fat as it distinguishes between subcutaneous and visceral fat deposits. Individuals with a higher percentage of visceral fat are more prone to metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding these physical signs and their implications can prompt individuals to take proactive measures to reduce their visceral fat levels.
Medical Tests
Medical professionals utilize various tests to accurately measure visceral fat levels within the body. Techniques like MRI and CT scans provide precise imaging for assessing visceral fat distribution. These imaging methods offer detailed insights into the amount and location of visceral fat, aiding in risk assessment and treatment planning. Regular health screenings, including blood tests for cholesterol and glucose levels, are essential for monitoring changes in visceral fat over time.
Regular check-ups are imperative in tracking visceral fat changes and overall health status. By staying proactive with medical evaluations, individuals can detect any alarming increases in visceral fat early on and implement lifestyle modifications accordingly to mitigate associated health risks.
Lifestyle Changes
Diet Modifications
Low-Carb Diet
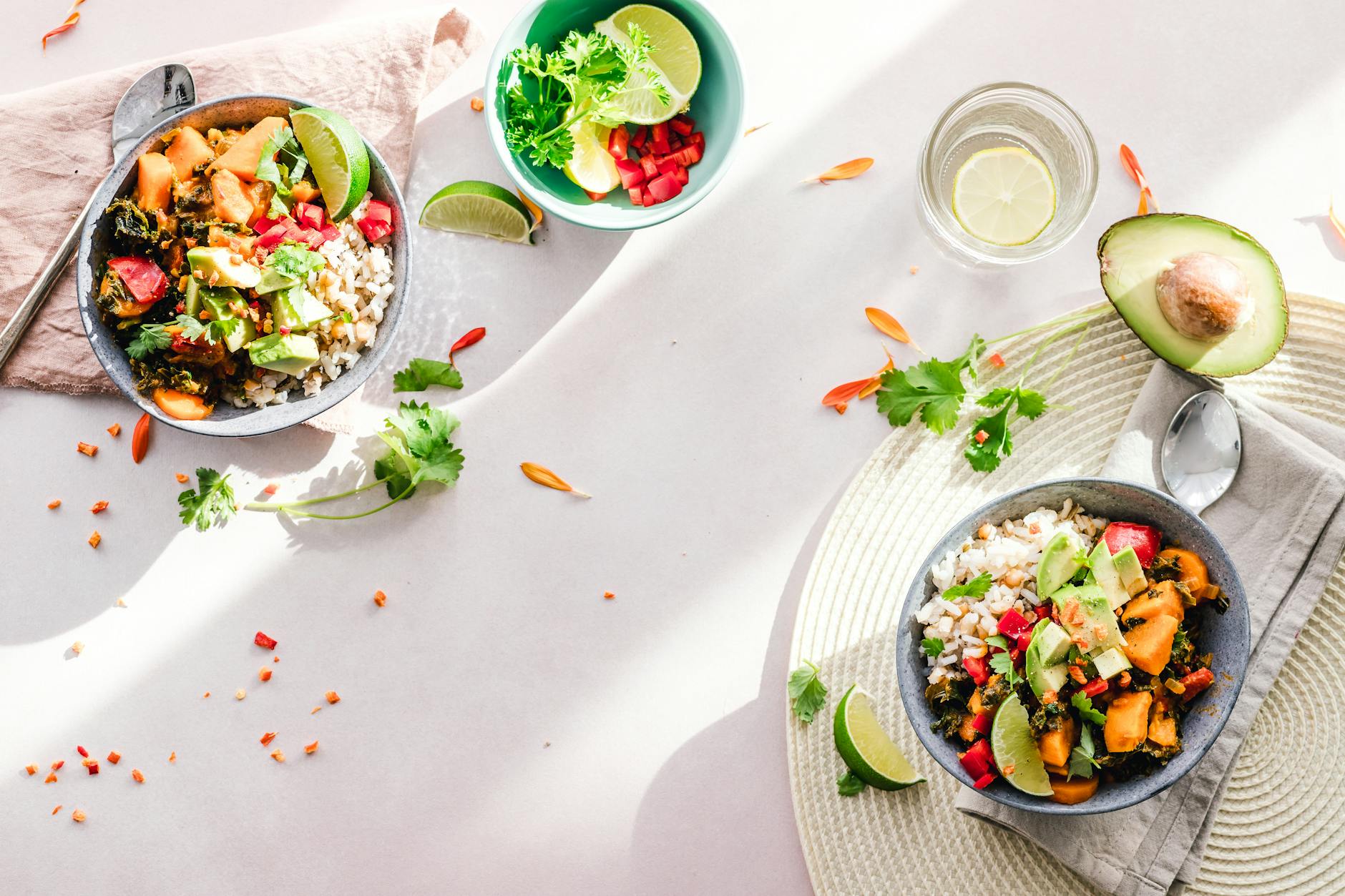

A low-carb diet is effective in reducing visceral fat by promoting the body to burn fat for fuel. Foods such as avocados, nuts, and seeds are suitable for visceral fat reduction due to their low carbohydrate content. Carbohydrate restriction leads to decreased insulin levels, which in turn reduces visceral fat storage.
Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber plays a crucial role in reducing visceral fat by binding with water to form a gel-like substance that slows down digestion and promotes fullness. Foods like oats, beans, and fruits are rich in soluble fiber and aid in visceral fat loss. By promoting satiety, soluble fiber helps manage weight effectively.
Protein Intake
Adequate protein intake is essential for reducing visceral fat as it boosts metabolism and preserves lean muscle mass during weight loss. Foods like chicken, fish, and tofu are recommended protein sources for optimizing visceral fat loss. Protein also helps control appetite and supports overall metabolic health.
Exercise Routines
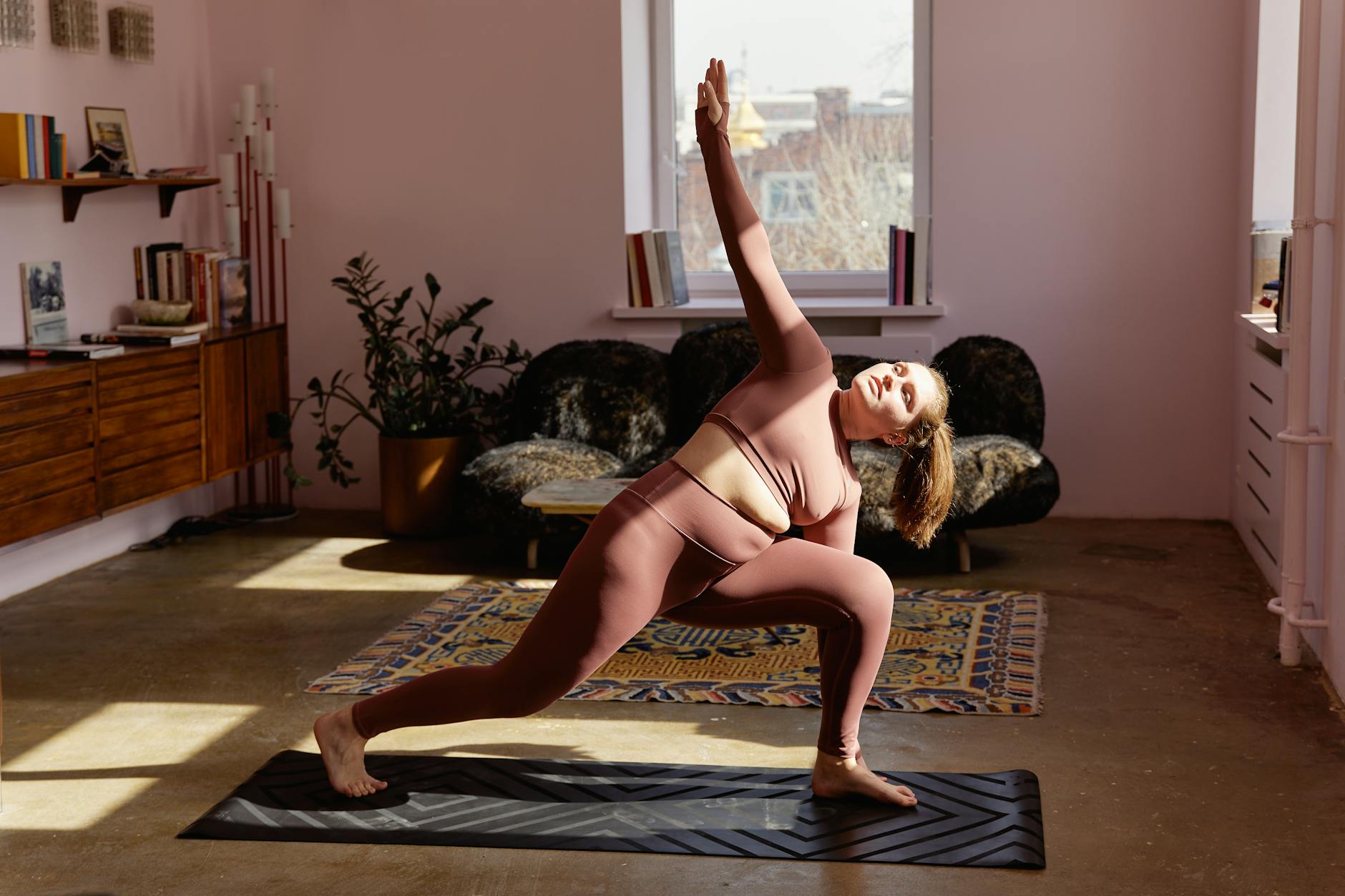

Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercises, such as running or cycling, are highly effective in burning visceral fat by increasing heart rate and oxygen consumption. Engaging in aerobic workouts for at least 30 minutes at moderate intensity can significantly contribute to fat loss. Regular aerobic exercise not only reduces visceral fat but also improves cardiovascular health.
Strength Training
Incorporating strength training into a fitness routine helps reduce visceral fat while increasing muscle mass, leading to a higher metabolic rate. Exercises like squats, lunges, and deadlifts target visceral fat deposits effectively. Long-term benefits of strength training include improved body composition and enhanced metabolic function.
Dietary Strategies
Sugar Reduction
Reducing sugar intake is crucial for decreasing visceral fat levels. Added sugars are directly linked to visceral fat accumulation due to their high caloric content. To support visceral fat loss, focus on minimizing sugary beverages, candies, and processed foods rich in hidden sugars.
Trans Fats Avoidance
Avoiding trans fats is essential as they significantly contribute to visceral fat accumulation and pose health risks. Common sources of trans fats include fried foods, baked goods, and margarine. Opt for healthier alternatives like olive oil, nuts, and seeds to reduce visceral fat deposition and improve overall health.
Probiotics Benefits
Probiotics play a vital role in promoting gut health and reducing visceral fat. These beneficial bacteria influence metabolism and fat storage in the body, aiding in weight management. Incorporate probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut into your diet to support gut health and combat visceral fat.
Behavioral Adjustments
Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly increase visceral fat levels due to its high calorie content. These extra calories often get stored as abdominal fat, contributing to overall weight gain. To support visceral fat loss, it is crucial to limit alcohol intake and opt for moderate consumption guidelines.
Sleep Quality
Quality sleep plays a vital role in regulating visceral fat levels. Inadequate sleep disrupts hormonal balance, leading to increased accumulation of visceral fat. Improving sleep hygiene by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment can help promote visceral fat reduction.
Stress Management
Chronic stress is closely linked to visceral fat gain as stress hormones trigger the storage of fat around organs. Effective stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and seeking social support, are essential for reducing visceral fat levels. By managing stress effectively, individuals can prevent excessive visceral fat accumulation and maintain overall health.
Advanced Methods
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting, a popular approach for reducing visceral fat, offers various benefits. It promotes fat metabolism and helps in weight loss. Different protocols like the 16/8 method or alternate-day fasting can be effective.
Incorporating intermittent fasting into your routine can aid in reducing visceral fat. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fasting regimen. By following a balanced diet during eating windows, you can maximize the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Impact on Surgeries
High levels of visceral fat can significantly impact surgical outcomes. Individuals with excess visceral fat face higher risks during surgeries, such as increased chances of complications and longer recovery times. Surgeons often recommend patients to reduce their visceral fat levels before undergoing any surgical procedures.
Reducing visceral fat before surgery is crucial for better post-operative outcomes and faster recovery. Lowering visceral fat levels can lead to reduced risks during surgeries and improve overall surgical success rates.
Implementation Tips
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting achievable goals is crucial for reducing visceral fat effectively. It’s essential to have realistic expectations to sustain long-term fat loss. To track progress, consider measuring waist circumference and body composition regularly. Adjust goals based on the results to stay motivated.
Monitoring Progress
Tracking changes in visceral fat over time is key to success. Methods like waist-to-hip ratio, DEXA scans, or bioelectrical impedance analysis can help monitor progress accurately. Stay motivated by celebrating small victories and focusing on overall health improvements.
Seeking Professional Advice
Consulting healthcare professionals such as doctors or nutritionists can provide personalized advice for managing visceral fat. Medical professionals play a crucial role in assessing visceral fat levels accurately through advanced techniques. Seeking guidance from trained experts ensures a safe and effective approach to visceral fat reduction.
Final Remarks
You now have a comprehensive understanding of visceral fat, its impact on health, and effective strategies to combat it. By identifying and addressing this deep-seated fat, you can significantly improve your overall well-being. Implementing lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and behavioral modifications will help you reduce visceral fat levels and lower associated health risks. Remember, consistency is key in achieving long-lasting results. Make small, sustainable changes that align with your goals and preferences to successfully combat visceral fat.
Take charge of your health today by incorporating the insights shared in this article. Start by making simple yet impactful changes to your daily routine and diet. Your efforts to combat visceral fat will not only enhance your physical appearance but also boost your overall health and vitality. Stay committed to these strategies, and you will soon experience the benefits of a healthier lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is visceral fat?
Visceral fat is a type of body fat that surrounds vital organs like the liver, pancreas, and intestines. It poses health risks as it can lead to various diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
How can one identify the presence of visceral fat?
Presence of visceral fat can be identified through waist circumference measurements or imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans. A waist measurement above 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women indicates a higher likelihood of having excess visceral fat.
What lifestyle changes can help reduce visceral fat?
Incorporating regular physical activity, managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption are key lifestyle changes that can aid in reducing visceral fat accumulation.
What dietary strategies are effective in targeting visceral fat?
Consuming a diet rich in fiber, lean protein, healthy fats, and low in added sugars and refined carbohydrates can help reduce visceral fat. Avoiding sugary beverages and processed foods is also beneficial.
How can behavioral adjustments contribute to reducing visceral fat?
Behavioral adjustments such as practicing mindful eating, setting realistic goals, staying consistent with healthy habits, and seeking support from friends or professionals can aid in reducing visceral fat over time.
Are there advanced methods available for targeting visceral fat?
Advanced methods like high-intensity interval training (HIIT), resistance training, and specific medical treatments prescribed by healthcare providers may be considered for individuals looking to target stubborn visceral fat deposits.
What are some implementation tips for effectively reducing visceral fat?
Implementing small but sustainable changes gradually, tracking progress regularly, staying motivated by focusing on overall health benefits rather than just weight loss, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or nutritionists can enhance the effectiveness of your efforts to reduce visceral fat.